Creating Agent Tools
Agent tools enable your agents to retrieve and process data from your Vectorize pipelines. This guide shows you how to create and configure tools through the Vectorize UI.
Overview
Tools are the bridge between your agents and your data pipelines. When an agent receives a query, it can call tools to:
- Search and retrieve relevant documents
- Apply metadata filters for precise results
- Process structured data from your pipelines
- Execute custom retrieval logic
Prerequisites
Before creating tools, you need:
- An active Vectorize organization
- At least one data pipeline with indexed content
- An agent
Creating Your First Tool
Step 1: Navigate to Tool Creation
- Go to Agents in the main navigation
- Select your agent from the list
- Click Create New Tool.
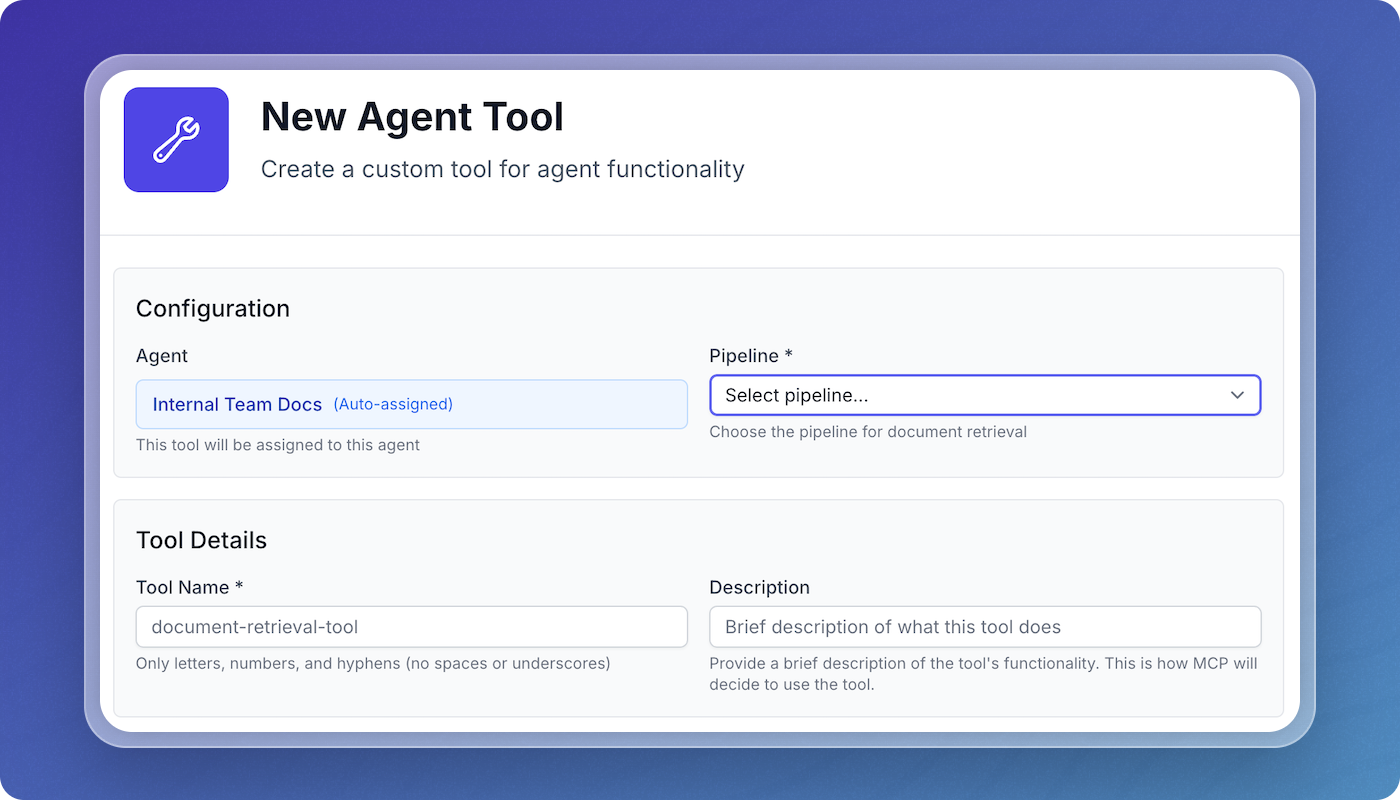
Step 2: Configure Basic Settings
Enter the core tool configuration:
- Pipeline: Select the data pipeline this tool will query
- Tool Name: A descriptive name (e.g.,
search-docs,find-runbooks) - Description: Clear explanation of what the tool does - this helps the LLM understand when to use it
Step 3: Understand Standard Parameters
Every tool automatically includes these standard parameters that are exposed to the LLM:
question(required) - The search query used to find relevant documents in the pipeline's vector indexk(optional) - Number of results to return (defaults to 10)rerank(optional) - Enable reranking for improved relevance using Cohere (boolean, defaults to false)mode(optional) - Search mode for Vectorize Built-In DB:vector(semantic search),keyword(text search), orhybrid(combined)
These parameters are automatically handled by Vectorize and don't need to be configured.
Step 4: Define Custom Input Parameters
In addition to standard parameters, you can define custom parameters for your tool to accept dynamic inputs from the agent. Common parameter types:
| Parameter Type | Use Case | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | Text queries, keywords | Search terms, document IDs |
number | Decimal values | Similarity score, price |
integer | Whole numbers | Result count, page number |
boolean | Toggles, filters | Include archived, exact match |
array | Multiple values | List of categories, tags |
object | Structured data | Complex filters, nested config |
enum | Fixed options | Document types, status values |
For each parameter, configure:
- Name: Parameter identifier (e.g.,
query,limit) - Type: Data type from the options above
- Description: What this parameter does
- Required: Whether the parameter is mandatory
- Default Value: Optional fallback value
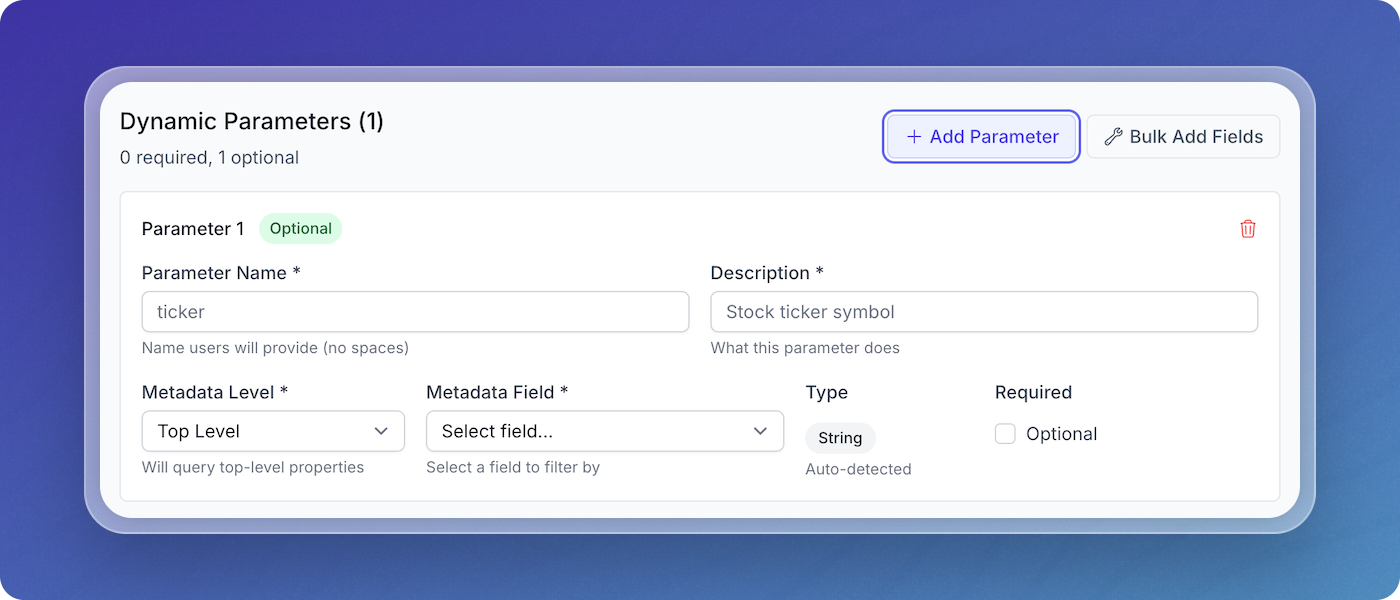 Configuring parameters for a search tool
Configuring parameters for a search tool
Step 5: Configure Dynamic Parameters
When creating custom parameters, you can link them to metadata fields in your pipeline. This creates automatic filtering based on the parameter values provided by the LLM.
For example, if you:
- Create a parameter named
service_name - Link it to the metadata field
serviceat the document level - When the LLM provides a value for
service_name, the tool automatically filters results to only documents wheredocument_metadata.servicematches that value
This allows you to create powerful, context-aware tools that filter results based on the specific information the LLM extracts from the user's query.
Step 6: Advanced Configuration
For more complex use cases:
- Link parameters to metadata: Connect custom parameters to your pipeline's metadata fields for automatic filtering
- Array parameters: Allow multiple values for more flexible queries
- Enum constraints: If a metadata field has predefined values, these become enum options for the parameter
- Required vs optional: Mark parameters as required or optional based on your use case
Step 7: Save Tool
- Click Save Tool to create the tool
- The tool is automatically assigned to your current agent
- You can assign the same tool to multiple agents from the Tools tab
Managing Agent Tools
Viewing Assigned Tools
From your agent's Tools tab, you can:
- See all tools currently assigned
- View tool configurations
- Monitor usage statistics
Adding Existing Tools
To reuse tools across agents:
- Go to the target agent's Tools tab
- Click Add Existing Tools
- Select from your organization's tool library
- Click Assign to Agent
Editing Tools
To modify a tool:
- Click the tool name from the Tools list
- Update configuration as needed
- Click Save Changes
Note: Changes affect all agents using this tool
Removing Tools
To remove a tool from an agent:
- Find the tool in the Tools list
- Click the Remove button
- Confirm removal
This only removes the assignment - the tool remains available for other agents.
Best Practices
Tool Naming
- Use descriptive, action-oriented names (
search-knowledge-base,find-customer-data) - Maintain consistent naming conventions across your organization
- Avoid generic names that don't indicate purpose
Descriptions
- Write clear descriptions that help the LLM understand when to use the tool
- Include example use cases in the description
- Specify what types of questions the tool can answer
Parameter Design
- Keep required parameters minimal
- Provide sensible defaults where possible
- Use enums for parameters with fixed options
- Include parameter descriptions that guide usage
Metadata Filters
- Align filters with your pipeline's metadata schema
- Use dynamic filters for flexibility
- Test filter combinations to ensure they return expected results
- Document available metadata fields for your team
Common Use Cases
Document Search Tool
Name: search-docs
Description: Search internal documentation and knowledge base
Custom Parameters:
- doc_type (string): Document category - linked to metadata field 'category'
- author (string): Document author - linked to metadata field 'author'
- status (enum: [draft, published, archived]): Document status - linked to metadata field 'status'
Behavior:
- When doc_type is provided, filters to documents where category matches
- When author is provided, filters to documents by that author
- When status is provided, filters to documents with that status
Customer Data Retrieval
Name: get-customer-info
Description: Retrieve customer account and interaction data
Custom Parameters:
- customer_id (string, required): Customer identifier - linked to metadata field 'customer_id'
- account_type (string): Account type - linked to metadata field 'account_type'
- date_range (string): Date range for filtering - linked to metadata field 'created_date'
Behavior:
- Always filters by customer_id (required parameter)
- Optionally filters by account_type and date_range when provided
Incident Runbook Finder
Name: find-runbooks
Description: Locate runbooks for incident response
Custom Parameters:
- service (string, required): Affected service - linked to metadata field 'service'
- severity (enum: [critical, high, medium, low]): Incident level - linked to metadata field 'severity'
- team (string): Responsible team - linked to metadata field 'team'
Behavior:
- Always filters to documents where service matches (required)
- Optionally filters by severity level and team when provided
- Enum values for severity come from the metadata field's predefined options
Integration Examples
MCP Agent Tools
When using tools with MCP agents in Claude Desktop or Cursor:
- Tools appear in the assistant's tool palette
- The assistant can invoke tools based on user queries
- Results are formatted and presented inline
- The assistant maintains conversation context with tool results
Chat App/Widget Tools
For chat interfaces:
- Tools are called automatically based on user messages
- The chat UI displays tool invocations
- Results are formatted with citations and sources
- Users can see which tools were used to answer their questions
Troubleshooting
Tool Not Returning Results
- Verify the pipeline has indexed content
- Check metadata filters match your data
- Test with broader queries
- Review parameter requirements
Tool Not Being Called
- Ensure tool description clearly explains its purpose
- Check that required parameters are being provided
- Verify the agent has the tool assigned
- Test with queries that explicitly match the tool's description
Performance Issues
- Limit result counts with appropriate defaults
- Use metadata filters to narrow search scope
- Consider splitting complex tools into simpler ones
- Monitor pipeline indexing status
What's Next?
- Configure MCP agents for development tool integration
- Set up chat interfaces with your tools
- Learn about metadata extraction to enhance filtering
- Explore learning paths for advanced agent capabilities